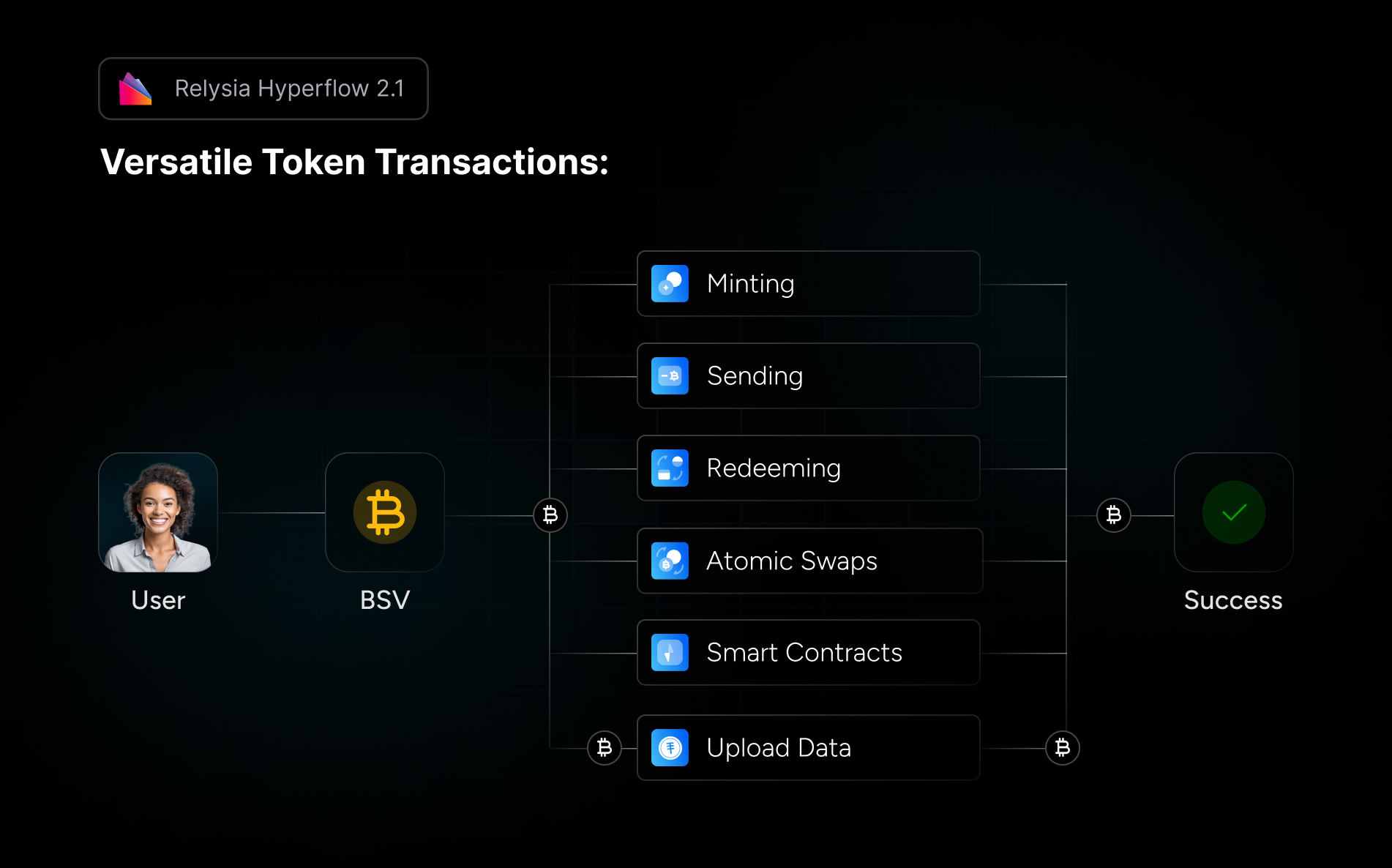
Core Properties of Blockchains
While it seems that there is a sheer amount of different blockchain protocols with different advantages, a closer inspection reveals that most of them fall into specific groups of economic incentive and scalability properties that make them unremarkably similar.
Game Theoretical Incentive
For the long term maintenance and functioning of a decentralized system, it is the incentive, not the narrative, that protects the system from collapse or takeover. Incentive system means, that when every player of the system acts in their own self interest, the system stays sustainable.
While that is obvious, few blockchains actually care about long term incentives and rather aim for short term gains or popularity of narrative.
Miners and infrastructure providers need to be incentivized to create better value to their costumers (the blockchain users) by scaling the network and lowering the fees of the network. Users, such as blockchain application developers need to have the guarantee of immutability, stability of the protocol and low transaction costs to ensure that they themselves can offer a valuable solution to their end costumers.
When end costumers are satisfied by the additional benefits of the blockchain, usage increases, and transaction through put demand rises. If they then combined pay more fees to the miners, the miners get incentivized to invest more into their infrastructure to provide a faster network at lower network costs.
If on the other hand miners don’t get incentivized to improve the user experience, and only compete against each other – may it be with proof of work hashpower of proof of stake investment, the network has no intrinsic property to grow towards a global infrastructure.
Why Bitcoin SV
Bitcoin SV has a simple but battle proven incentive system. Blocks are not limited by protocol developers, but purely by miners that orient their own infrastructure investment (to increase server capacities and network throughput) based on reward expectations (which is the transactions * fee). If some miners process too big blogs for others to process, other miners will orphan those blocks and keep mining their own perceived honest branch.
Users on the other hand can expect a decrease in fees and a constant increase in maximum transaction capabilities (based on moores law) and thus rely on the Bitcoin SV protocol as a long term infrastructure solution. It may sound simple, but its those simple insights that are often over seen but painfully critical once developing a system of scale. One cannot build a world spanning global network without getting the basics right, and at closer look very few seem to focus on real world adoption.